Fighting and Winning Wars in the Cyber Age

The
world has seen a tremendous transformation in the field of warfare since WW-II
and a constant influx of new technologies continues to transform and complicate
the modern battlefield. Governments and militaries around the world are seen
scrambling to grapple with the challenges posed by the unprecedented demands of
modern warfare and to accrue optimum benefits from the endless opportunities
brought about by the technological revolution.
However, the most influential and consequential change brought about
this technological revolution is the introduction of cyberspace into the
existing domains of warfare. Today, every conventional domain of warfare, i.e.
land, air, maritime and space, largely depends on cyberspace for its operations
and success. Modern militaries across
the globe have become an easy target for hackers, cyber criminals backed by
rogue regimes, terrorists, state and NSAs (Non-State Actors), who can possibly
infiltrate, degrade, disrupt and even halt critical military operations during
peace and war. The alarming pace of AI
evolution in military affairs and especially in cyberspace is likely to further
complicate the scenario making it extremely difficult to safeguard critical
military operations. This extra ordinary reliance of modern warfare on cyberspace
demands extra ordinary measures by the governments in general and militaries specifically
to be able to fight and win in the cyber age.
The
Changed Face of Warfare
The
technological revolution since the end of Second World War continues to
transform warfare at an unprecedented pace. Every technological innovation in
the conventional domains of warfare has brought with it its own opportunities
and challenges. However, in modern military operations, cyberspace has totally
transformed the face and character of warfare. US DoD defines cyberspace as a
global domain within the information environment consisting of the
interdependent network of information technology infrastructures and resident
data, including the Internet, telecommunications networks, computer systems,
and embedded processors and controllers. Today, militaries are equipped with state-of-the-art
weapon systems capable of operating and influencing the battlefield at far off
distances without getting into direct contact with the adversary. Stealth
fighters and bombers equipped with beyond visual range (BVR) weaponry,
ballistic missiles and long-range guided weapons, laser guided munitions, smart
munitions, kamikaze drones, HALE (High Altitude Long Endurance) and MALE
(Medium Altitude Long Endurance) UAVs, loitering munitions, advanced AEW&C
platforms, ISR/EW assets, modern battle tanks, sophisticated aircraft carriers
and warships, all supported by land-based or satellite-based connectivity and
run by the most advanced computing power, form the backbone of modern
battlefield. Strengths of all these modern weapon systems and weapons are best
exploited through the concept of Network Centric Warfare (NCW) that connects
and enables all conventional domains of warfare through cutting-edge technology
to provide a comprehensively fused real-time picture in the contemporary
command and control centers. These command-and-control centers are the hub of
military activity and hold a pivotal position for decision makers responsible
for the conduct of modern wars. Any breach in this fabric of Network Centricity,
which runs from tactical to strategic level and woven around cyberspace, can
cripple any military operation today.
This technological revolution of
21st century has transformed warfare and changed the face of the
modern battlefield where wars are no longer confined to physical confrontations
on a geographically defined battlefield. Today, almost every military
capability including weapon systems, command and control centers etc., that
utilize connectivity and computing, is vulnerable to a cyber-attack by the
adversaries. Recent Israeli “pager attacks” against Hezbollah have proven that
even individual military leaders r key political figures using some sort of
computer or EM-based device i.e. cell phones, walkie talkies or pagers could be
targeted through careful planning and execution.
Russia–Ukraine war has witnessed
some of the most extensive cyber operations in modern history. Russian
cyber-attack against Kyivstar in 2023, Ukraine’s largest telecom provider[i],
and Ukraine’s cyber operations of 2024 against Russian financial institutions,
internet providers, and municipal administrations[ii]
indicate the enormous potential of cyber operations in modern warfare. Likewise,
around 480 cyber-attacks are presumed to have taken place during the 04-day
conflict between India and Pakistan in May 2025[iii].
Israel and Iran conflict of June 2025 saw a devastatingly effective use of
cyber operations against Iranian command and control, banking and missile
infrastructure[iv]. Iranian
groups also engaged in extensive cyber operations against various Israeli
entities with varying and unverifiable success.[v]
It is worth noting that unlike
other conventional domains of war where enemy movements, capabilities and
preparations can be tracked through advanced intelligence gathering
capabilities, cyberspace does not offer these luxuries. You can never know what
the adversary is planning or is capable of, until he strikes your assets. State
and non-state actors continue to work during peace time gathering knowledge
about their potential targets and exploring loopholes in cyberspace to be able
to attack at the time of their choosing without any pre-warning. Also, the
absence of comprehensive international legislation to counter cyber threats
makes it easier to exploit this domain without the fear of attribution. Since cyberspace cuts across all conventional
domains of warfare and is their prime enabler, thus securing cyberspace has
become the key to ensuring success across all other domains of warfare.
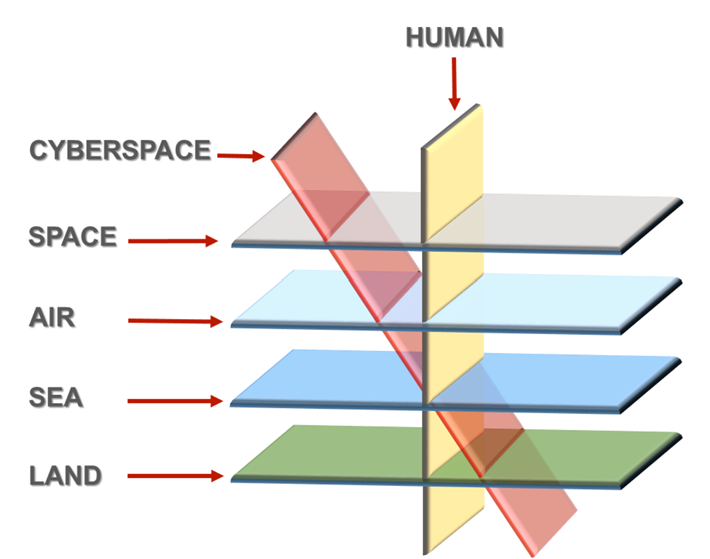
Preparing
to Win in the Cyber Age
The
unprecedented challenges and complications posed by the vulnerabilities of cyberspace
demand extraordinary measures by the governments and militaries to prepare and
win wars in the cyber age. While most of
the militaries operate on closed-loop networks with limited connectivity to the
outside world, still military systems continue to be vulnerable to
cyber-attacks. Insider threat, compromised hardware/software, non-adherence to
the Sops and policy guidelines, a possible breach through the wireless nodes
and portable devices, continue to be the major vulnerabilities in the military
systems requiring a continuous effort by the cyber professionals to secure
military operations. Although many
militaries have their own cyber warfare departments and commands working round
the clock to ensure security of the military cyberspace, yet there always
remains a room for improvement and frequent incidents of cyber-attacks against
military systems across the globe bear witness to it. In light of the most
common vulnerabilities of military cyberspace, following are few
recommendations that can help in securing military operations in the cyber age:
–
(a) Comprehensive Cybersecurity
Strategy and Foresight
History is a witness that success of military operations has always depended
upon the quality of military strategy, strategic guidance and strategic
foresight of military leadership to predict threats and challenges and be
prepared for them through employment of smart strategies. Similarly, preparing
to counter threats in cyberspace requires a comprehensive cybersecurity
strategy that combines the strengths of all available capabilities to address
existing vulnerabilities through state-of-art technical and policy solutions
implemented by the best available cyber professionals. The cybersecurity
strategy must be a living organism that needs to be updated and modified
depending upon the changing environment in the international cyberspace where
new technologies, new threats and new attack mechanisms are born on almost
daily basis. Military leaders must foresee future trends based on available
information and start preparing for them now instead of waiting for something
to happen and then embarking upon a firefighting mission when the damage has
already been done. A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy formulated after
involvement of all the stakeholders and implemented across the board with
frequent feedback mechanisms, shall decide the level of cybersecurity in a
military organization. A proactive
cybersecurity mindset coupled with a sound cybersecurity strategy shall prove
to be of immense value for any military today.
(b) Staying Abreast with
Technological Evolution The pace of technological evolution in
cyberspace is mindboggling, and keeping up with it or trying to stay ahead of
it is extremely challenging but a key to success and security. Military
organizations must try to stay abreast of the technology curve and should keep
on frequently assessing the technical quality of the existing hardware and
software both in offensive and defensive realms of cybersecurity. Employment of
the latest available technologies that cater for the existing and foreseeable
threats should keep military operation safe and resilient in cyberspace. Round
the clock monitoring systems supported by latest firewalls, encryptions, and
intrusion detection systems coupled with regular vulnerability assessments and
rapid response mechanisms shall keep the military operation up and running
while considerably reducing the effectiveness of a cyberattack. Maintaining
offensive cyber capabilities is also vital as it not only prepares you to mount
a formidable defense but also equips you with the latest offensive techniques
that may be put into action when required. For example, employment of AI is
seeing an exponential rise and AI-driven cybersecurity systems are
revolutionizing both offensive and defensive cybersecurity. While machine
learning algorithms can help in detecting anomalies in real time, predict
potential threats, and automate responses, AI can also be utilized to launch
sophisticated phishing campaigns, develop deepfake technology, and automate
cyber-attacks, which would make security of cyberspace extremely complex and challenging.
Militaries should also develop elaborate forensics facilities to scan the newly
procured hardware and software that have been procured off the shelf for
critical infrastructures and systems. Militaries must always be on the lookout
for latest technologies, invest in innovation and R&D, indigenize where
possible and get help from the private sector professionals to stay abreast of
the latest trends and maintain technological superiority as far as possible.
(c) Education / Training
Regardless of the rapid advances being made to incorporate AI in the
offensive and defensive cybersecurity realms, need for highly qualified and
trained cyber professionals shall remain of pivotal importance to ensure
success of modern military operations. Establishment of cyber warfare academies
and cyber commands across many militaries across the world are the steps to
keep military cyber professionals abreast with latest offensive and defensive
cybersecurity methods and technologies. However, militaries must engage private
sector experts and employ latest cyber security training platforms (Cyber
Ranges) specifically designed for imparting near-real-time offensive and
defensive cybersecurity trainings. Platforms that are not only capable of
meeting the latest cybersecurity education and training requirements but are
also ideally suited for conducting live simulated cyber exercises and wargames
at organizational as well as national level.
While most of the Cyber Range Platforms (Cyberranges, Circadence,
Cyberbit etc) available in the market today are generally cloud-based and may
not address the security concerns of militaries. On-premises platforms (PriviaHub
etc) could be an ideal solution for educating and training cyber professionals
through near-realistic simulations and exercises. Peace-time proactive training
and preparation are the key to safeguarding cyber space in the current volatile
digital environment. Therefore, militaries should not shy away from investing
in the latest education and training platforms as it could make a difference
when it comes to winning wars in the cyber age.
(d) Cybersecurity awareness and
Policy Implementation
Military organizations must run elaborate cybersecurity awareness programs
across the organization to educate common users of the potential cost of
carelessness, and non-adherence to the laid-out Sops, policies and best
practices. Similarly, policies and procedures must be frequently revised and
updated in consultation with the experts keeping in view the latest changes
across the organization and introduction of new technologies. There must be clear policies and rules on how
the defaulters would be dealt with and those contributing positively would be
rewarded to motivate common users to adhere to the existing policies and
guidelines. There must also be an elaborate intelligence and monitoring
mechanism to cater for the insider threat which happens to be one of the most
lethal threats in cybersecurity. Regular cybersecurity audits conducted by
reputable professional organizations and periodic cybersecurity exercises can
be tremendously helpful in determining the robustness of existing protocols and
policies and identifying vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Owing
to the ongoing technological revolution, the world has witnessed an incredible
transformation in warfare over the past few decades. One of the major elements responsible for
this transformation is the advent of cyberspace, as a vital domain of warfare,
which today is the driving force behind all the conventional domains. Warfare
in the cyber age has shifted from physical battlefield to digital battlefields.
Success on the digital battlefield is now the guarantor of success and victory
on the physical battlefield. Military success
in the cyber age has come to depend on mastering this new domain, the
cyberspace. A combination of measures, including a sound cybersecurity
strategy, strategic foresight, technological superiority, proactive approach,
training, education and private-public-partnership are some of the key elements
that would help in fighting and winning wars in the cyber age.
[i]
Kott, A., Dubynskyi, G., Paziuk, A., Galaitsi, S. E., Trump, B. D., &
Linkov, I. (2024). Russian Cyber Onslaught was Blunted by Ukrainian Cyber
Resilience, not Merely Security. arXiv preprint. https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.14667.
[ii]
Wilner, A. S., Williams, G., Thuns-Rondeau, M., Beaulieu, N., &
Cossette-Sharkey, V. (2024). Offensive Cyber Operations and State Power:
Lessons from Russia in Ukraine. International Journal. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00207020241234228.
[iii]
https://cybelangel.com/blog/india-pakistan-cyber-conflict/.
[iv]
https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/what-the-israel-iran-conflict-revealed-about-wartime-cyber-operations/.
[v]
Ibid